while True Loop
EXAMPLE (THIS WILL NOT STOP) :
while True:
print("This program is running")
print("Aww, I was having a good time 😭")
MAKE IT STOP
There is a way to stop the loop with the word
break. This exits the loop and stops all code at that point. Even if there is more code written after break that is inside the loop. 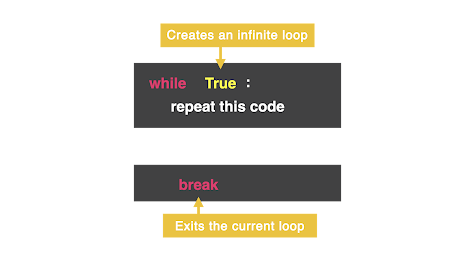 |
EXAMPLE :
while True:
print("This program is running")
goAgain = input("Go again?: ")
if goAgain == "no":
break
print("Aww, I was having a good time 😭")
Comments
Post a Comment